What is the Air Quality Index (AQI)?
AQI - The U.S. AQI is Environmental Protection Agency’s index for reporting air quality.


Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) establishes an Air Quality Index (AQI) for five major air pollutants regulated by the Clean Air Act. Each of these pollutants has a national air quality standard set by EPA to protect public health:
-
Ground-level ozone Ozone: Good Up High, Bad Nearby (epa.gov)
-
Carbon monoxide
-
Sulfur dioxide
-
Nitrogen dioxide
-
particle pollution (also known as particulate matter, including PM2.5 and PM10)

Particle pollution — also called particulate matter (PM) — is made up of particles (tiny pieces) of solids or liquids that are in the air. These particles may include:
-
Dust
-
Dirt
-
Soot
-
Smoke
-
Drops of liquid

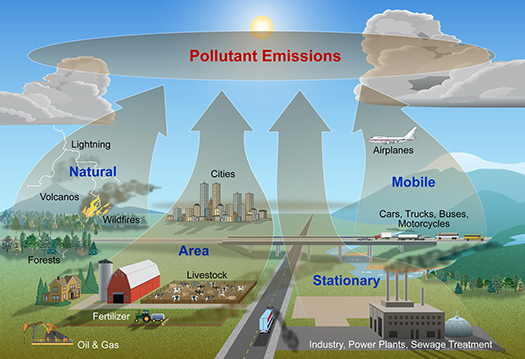
Photo Credit: National Park Service | https://www.nps.gov/subjects/air/sources.htm
What is Air Pollution?
-
Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical, or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.
Why is it so important to reduce air pollution?
-
Air pollution is the largest environmental risk to public health globally. Exposure to particulate matter air pollution causes an estimated 6.7 million premature deaths each year, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Where does air pollution come from?
Air pollution comes from a wide array of sources, both natural and caused by human activities.
- Natural sources include:
- Volcanic eruption
- Soil and desert dust
- Wildfires
- Lighting
- Human sources include:
- Power generation
- Transportation
- Industry
- Agriculture
Who is more at risk of air pollution?
-
People with pre-existing health conditions (e.g. cardiorespiratory)
-
Children and pregnant women
-
Elderly
-
Outdoor workers
For more information on Health Effects of Air Pollutants on Vulnerable Populations, visit https://www.epa.gov/air-research/research-health-effects-air-pollution
How is Smog Formed?
- Ground-level ozone, the primary ingredient of smog, results from the chemical reactions of reactive organic gases and oxides of nitrogen in the presence of sunlight. The following equation represents smog formation:
-
Reactive Organic Gases + Oxides of Nitrogen + Sun = Smog (Ozone)
-
What is the biggest problem with Air Pollution?
-
Air pollution can affect lung development and is implicated in the development of emphysema, asthma, and other respiratory diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).

